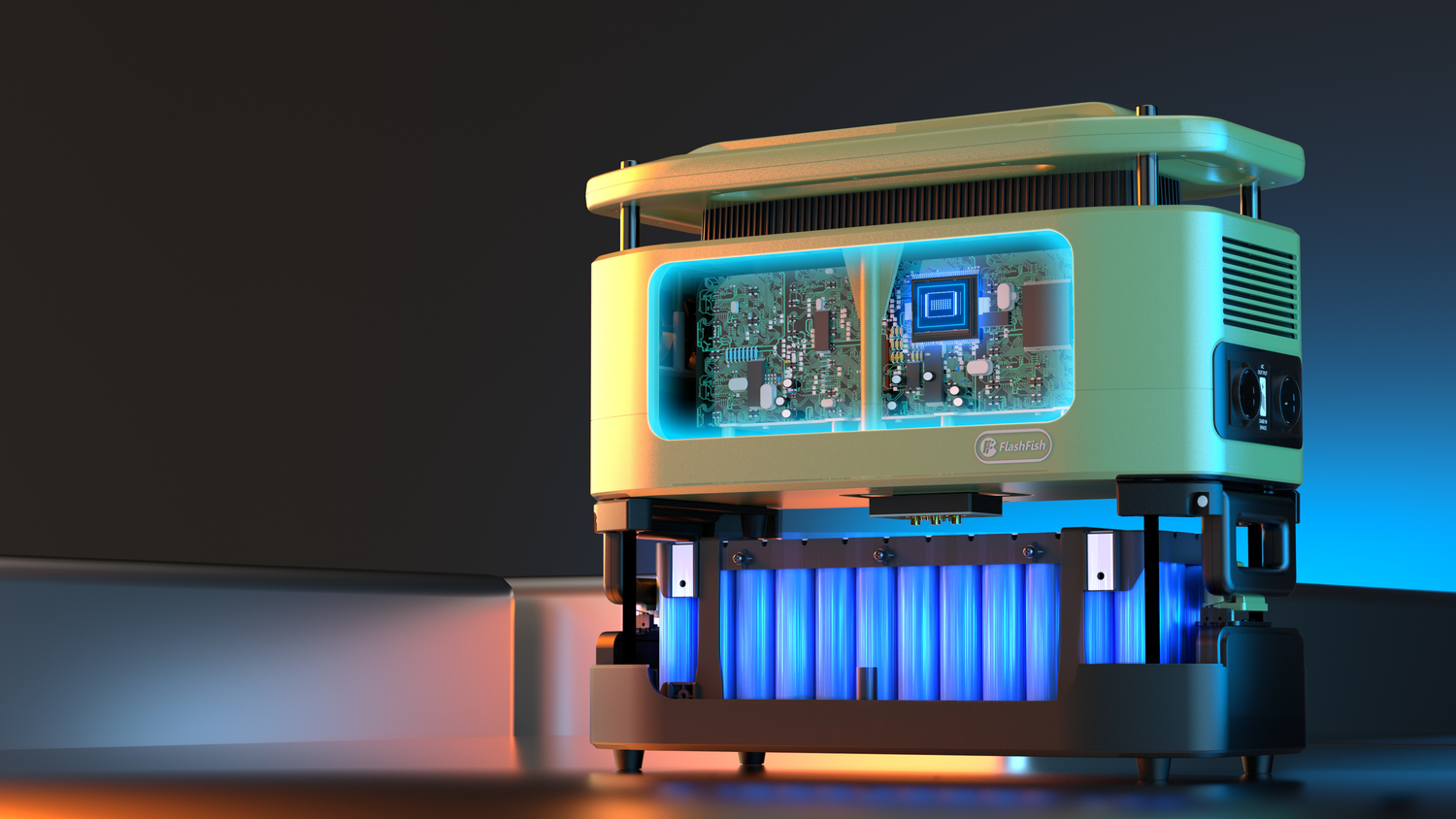
Physical Condition:
Check for any physical damage such as cracks, dents, or bent components.
Inspect the overall cleanliness of the inverter. Accumulation of dust or debris might indicate poor maintenance or ventilation issues.
Ensure that all screws, connectors, and fasteners are properly tightened and secured.
Component Inspection:
Look for any signs of overheating, such as discoloration or burn marks on components.
Check for swollen or leaky capacitors, which may indicate a failure.
Inspect the solder joints on the PCB for cracks, cold solder joints, or any signs of corrosion.
Examine the wiring and connections for any signs of fraying, overheating, or loose connections.
Labeling and Markings:
Read the labels and markings on the inverter to identify its model number, specifications, and ratings.
Ensure that the labeling matches the manufacturer's specifications and that there are no discrepancies.
Cooling System:
Inspect the cooling fans and heat sinks for any blockages, dust buildup, or damage.
Check if the cooling system is functioning properly to prevent overheating issues.
Enclosure Integrity:
Examine the enclosure or casing of the inverter for any cracks, gaps, or signs of damage.
Ensure that the enclosure provides adequate protection against environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and debris.
Manufacturer's Labels and Certifications:
Look for labels or certifications from reputable testing organizations such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or CE (Conformité Européenne) to verify compliance with safety and quality standards.
Ensure that the inverter meets relevant industry standards and regulations.
Comparative Analysis:
If available, compare the visual condition of the inverter with similar models or units to identify any noticeable differences or anomalies.
While visual inspection can provide useful information, it may not reveal all potential issues with the inverter. Therefore, it's essential to complement visual checks with functional testing and diagnostics to ensure the overall quality and reliability of the device. If you notice any significant concerns during the visual inspection, it's advisable to consult with a qualified technician or engineer for further evaluation and repair.






























Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.